Compression Effects
Blood Circulation
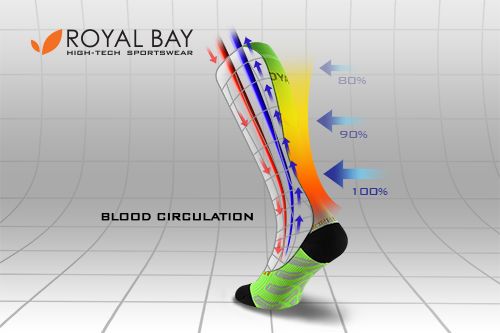
-
Improves venous return and blood circulation in muscles
Compression pushes blood faster from the muscle bloodstream into large arteries and veins. Graduated compression then promotes venous return and facilitates the distribution of oxygenated blood to the muscle. -
Accelerates removal of lactic acid
Faster blood circulation in the muscle speeds up removal of metabolites. This helps the muscle to regenerate and deal with heavy strain during exercise. -
Delays the onset of fatigue and speeds up regeneration
Thanks to the faster removal of metabolites (especially lactate), the onset of metabolic acidosis (muscle fatigue) is delayed, while compression accelerates muscle regeneration after exercise.
Muscle Stabilization
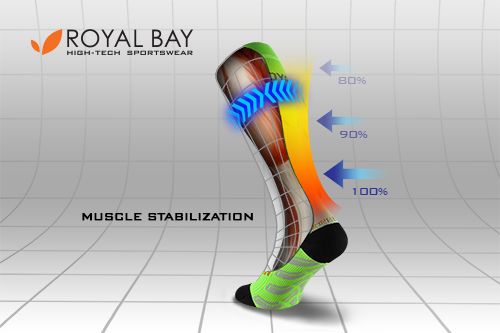
-
Stabilizes muscles during exercise
A fixed supported muscle better handles shocks during sports performance. -
Reduces the risk of muscle injury
The muscle is less susceptible to microtrauma that may occur in endurance or otherwise extreme strain.
Muscle Activation
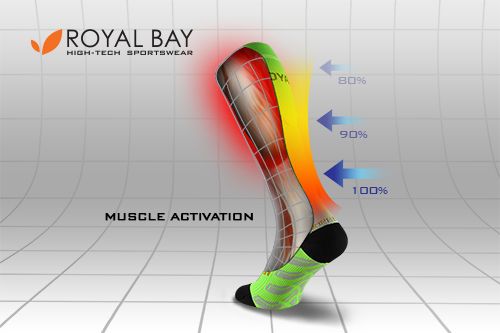
-
Activates the muscle before exercise
By applying compression, the muscle is better supplied with blood, while staying warm thanks to the thermoregulatory properties of our products. This makes the muscle always perfectly ready for any performance.
Protection on Travels
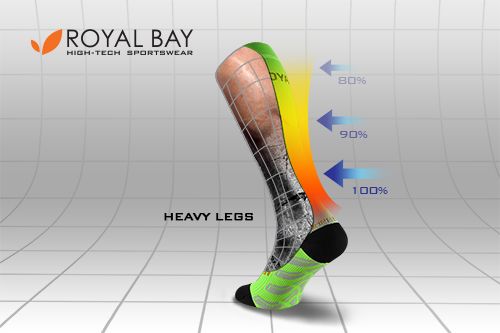
-
Removes the feeling of heavy legs
After a long drive, you may feel your muscles are stiff and heavy, which is not an ideal condition before performance. Compression in this case helps to keep your muscles activated and filled with blood, helping you to avoid stiffness and leg swelling. -
Prevents travel thrombosis
When travelling by plane, you are exposed to an increased risk of travel thrombosis. Sports compression products significantly reduce the risk.